Taxonomic reassessment of the Indo-Pacific Scytosiphonaceae (Phaeophyceae): Hydroclathrus rapanuii sp. nov. and Chnoospora minima from Easter Island, with proposal of Dactylosiphon gen. nov. and Pseudochnoospora gen. nov.
Abstract
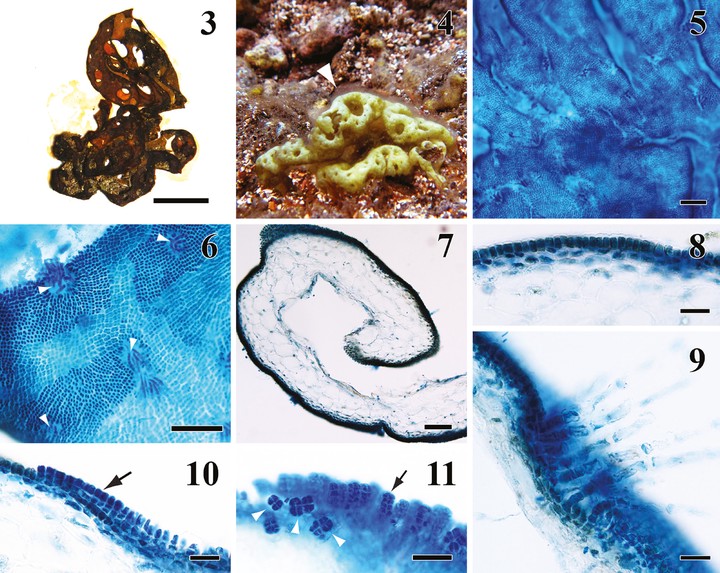
A new and putatively endemic species of Hydroclathrus, Hydroclathrus rapanuii, is described from the geographically isolated Easter Island in the southeastern Pacific based on morphological and molecular phylogenetic data. It is distinguished from other Hydroclathrus by thalli of unevenly furrowed thin membranes, and angular, block-like plurangial sori. Our phylogenetic analyses indicated that H. rapanuii is closely related to the generitype Hydroclathrus clathratus. We also report on the morphology and phylogeny of Chnoospora minima from Easter I. and elsewhere in the Indo-Pacific Ocean, noting the previously unreported presence of hollow portions in its medulla. Although not collected from Easter I., we herein propose the recognition of two new genera, Dactylosiphon gen. nov. and Pseudochnoospora gen. nov., based on our three-gene phylogeny and their known morphologies and anatomies. Dactylosiphon is based on the three species currently assigned to Colpomenia (C. bullosa, C. durvillei, and C. wynnei) that are genetically and morphologically (i.e. thalli with erect and finger-like tubes arising from a common saccate base) distinct from other members of Colpomenia. The monotypic genus Pseudochnoospora is represented by the decumbent, branching, and inter-adhesive species currently known as Chnoospora implexa. With the above proposals, we further increase the genus-level diversity of Scytosiphonaceae in the Indo-Pacific Ocean.